Blockchain in Biobanking
Explore how blockchain enhances data security, interoperability, clinical trials, biobanking, and more in healthcare and medical research
Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology offers several promising applications in healthcare, with potential benefits in various areas:
Data Security and Privacy: Blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger, enhancing the security and privacy of patient health records. Cryptographic methods protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Interoperability: Blockchain can facilitate interoperability among different healthcare systems by creating a unified, immutable record of patient data. This allows for seamless information sharing across various providers and systems while maintaining data integrity.
Clinical Trials and Research: Blockchain improves transparency and reliability in clinical trials by securely recording data such as patient consent and trial results. This reduces the risk of data manipulation and ensures research findings are credible.
Supply Chain Management: In pharmaceuticals, blockchain can track the entire supply chain of drugs, from manufacturing to delivery. This helps verify the authenticity of medications, prevent counterfeits, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Insurance Claims and Billing: Blockchain streamlines the insurance claims process by providing a transparent and automated system for verifying and processing claims. This reduces fraud, lowers administrative costs, and speeds up provider reimbursement.
Patient Empowerment: Blockchain enables patients to control and manage their health data more effectively. It facilitates better communication with healthcare providers and allows patients to take an active role in their healthcare decisions.
Consent Management: Blockchain simplifies managing and recording patient consent for medical procedures and data sharing. Smart contracts can automate consent processes and ensure permissions are accurately documented and respected.
Biobanking and Research: Blockchain can enhance biobanking by providing a secure, transparent way to track and manage biological samples. It allows researchers to maintain an immutable record of sample provenance, consent, and usage. This improves the integrity of biobanks, facilitates sample sharing, and ensures compliance with ethical standards and regulations.
In summary, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enhancing data security, streamlining processes, and improving transparency. Its applications extend to biobanking, where it can significantly benefit research by improving sample management and integrity.

Blockchain in Biobanking
Webinar
“Using Blockchain to give people the most secure, private, and complete control of their BioData”. Daniel Uribe MBA, CEO of GenoBank.io | Biosample Hub webinar, 25th April, 2024
Summary
Daniel, CEO and co-founder of GenoBank.io, gave this webinar on the 25th April 2024. He kicked off by introducing himself and sharing how he became involved in blockchain technology. In 2015, during an executive program at Singularity University in Silicon Valley, Daniel first encountered blockchain, thanks to Peter Diamandis, a leading advocate for exponential technologies. Inspired by this, Daniel moved to Palo Alto to explore how blockchain, particularly its cybersecurity applications, could enhance security in various fields.
In 2017, his career path took a personal turn when his youngest son was diagnosed with a rare blood disease. This diagnosis, confirmed through a DNA test, inspired Daniel to delve into the world of genomics and explore how blockchain could protect sensitive genomic data, laying the foundation for what would later become GenoBank.io.
The Creation of GenoBank.io
Following his son’s diagnosis, Daniel launched GenoBank.io in 2018 with a clear mission: to provide individuals with secure control over their genomic data through blockchain in healthcare. He introduced the concept of the “bio wallet,” a secure digital tool similar to a cryptocurrency wallet but designed to store genomic information. The bio wallet ensures that users can protect and manage their most sensitive data, controlling who can access it.
This approach addresses the rising concern around safeguarding personal biodata in a world where data breaches and privacy violations are increasingly common. GenoBank.io, through its bio wallet, gives individuals a practical solution to these challenges.
Blockchain in Healthcare
Daniel explained how blockchain, initially known for financial transactions, has vast potential in healthcare, particularly in genomics. GenoBank.io uses blockchain to create Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) that represent each biosample. These Bio NFTs store crucial information such as the donor’s consent, terms of use, and specific characteristics of the biosample. This approach makes it easy to track and manage consent, ensuring that every sample is linked to a verifiable digital record.
Tokenization, Daniel emphasized, is not a new concept but one that blockchain enhances by adding transparency and immutability. In healthcare, particularly genomics, tokenization ensures that each sample’s use is compliant with the donor’s wishes and can be publicly verified.
Ethereum and Smart Contracts
Daniel further explained why GenoBank.io uses the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum’s flexibility in executing smart contracts makes it ideal for managing complex agreements like consent forms in healthcare. These smart contracts automatically enforce terms and conditions, giving patients confidence that their data is being used appropriately.
He illustrated how GenoBank.io uses smart contracts to track each biosample’s usage through Bio NFTs. These tokens act like digital licenses, specifying what the sample can be used for, whether for research or commercial purposes. If a donor chooses to revoke their consent, the smart contract ensures that the sample’s access is immediately restricted.
Privacy Protection
Daniel highlighted how blockchain in healthcare enhances privacy. While the blockchain stores details of the consent and agreement, no personal identifying information is kept on the blockchain itself. Instead, a cryptographic wallet protects the donor’s identity, allowing them to remain anonymous. This ensures that the genomic data is securely stored and accessible only to authorized parties.
The use of cryptographic tokens simplifies the management of access rights. Daniel described how the process ensures that biosamples can only be accessed by authorized individuals, adding another layer of protection and transparency to the system.
Addressing Challenges
Daniel acknowledged potential challenges that arise with blockchain-based systems, such as the risk of losing cryptographic keys, which provide access to data. He explained that if a donor loses their key, a new sample can be provided, and a DNA test will match the donor’s genetic signature, allowing them to regain access.
When a donor revokes consent, the corresponding token is deactivated. This removes access to the biodata stored on the blockchain. If any unauthorized party has a copy of the data, privacy laws like GDPR ensure further legal protection for the donor.
Integrating AI
Looking to the future, Daniel discussed how AI could work alongside blockchain to empower patients. He sees AI playing a critical role in helping patients understand their genomic data. By integrating large language models, such as ChatGPT, AI could simplify the process of interpreting complex genetic information for patients, bridging the gap between medical professionals and individuals.
Parents, for example, could use AI tools to better understand the significance of genetic markers or health conditions present in their children’s DNA. This would allow them to make more informed decisions about their healthcare.
Ensuring Compliance and Reducing Friction
Blockchain in healthcare has another major benefit—ensuring legal compliance across different regions. Daniel noted that GenoBank.io is designed to meet strict regulatory standards like GDPR in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). This ensures that biobanking organizations can share data with confidence, knowing that it complies with various legal frameworks.
He also pointed out how blockchain can streamline the process of sharing data across borders, reducing friction when navigating different data laws. With blockchain, the consent process is transparent and verifiable, allowing for smoother data exchange between countries and institutions.
Q&A Session
During the Q&A, Daniel addressed several insightful questions about how blockchain in healthcare can address common concerns. For instance, he explained how GenoBank.io could handle disputes, such as separating parents or families inheriting genomic data. He reassured participants that programmable tokens could be designed to adapt to specific legal or family circumstances.
He also emphasized that while blockchain-based systems still face some challenges, particularly regarding adoption and ease of use, the benefits of secure, patient-controlled biodata far outweigh these obstacles. In cases of inherited genomic data, blockchain technology provides a robust framework for managing the transfer of ownership and consent.
Conclusion
Daniel concluded the session with optimism, stating that blockchain in healthcare, combined with AI, will transform the biobanking industry. By giving patients full control over their genomic data, blockchain enables a more transparent, secure, and collaborative ecosystem between individuals, researchers, and healthcare providers.
He invited participants to continue the conversation and explore how blockchain in healthcare will evolve, offering personalized demos for those interested in learning more about GenoBank.io’s platform.
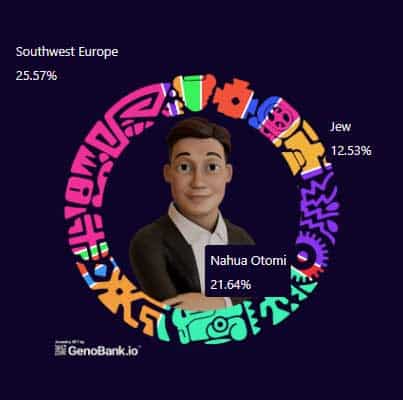
See the Genobank.io Web3 Biosample Attributions Explorer